3.2 KiB
Executable File
3.2 KiB
Executable File
| Singly linked list (SLL) | Doubly linked list (DLL) |
|---|---|
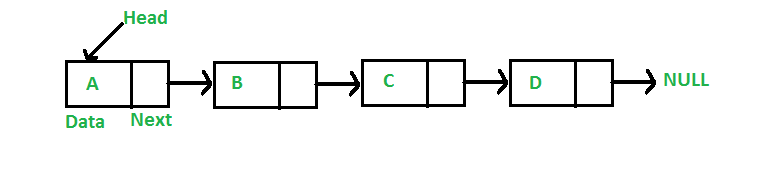
| SLL nodes contains 2 field -data field and next link field. | DLL nodes contains 3 fields -data field, a previous link field and a next link field. |
 |
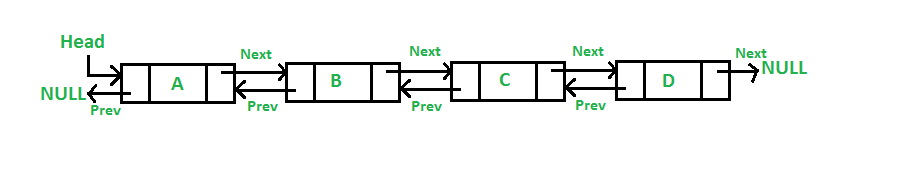 |
| In SLL, the traversal can be done using the next node link only. Thus traversal is possible in one direction only. | In DLL, the traversal can be done using the previous node link or the next node link. Thus traversal is possible in both directions (forward and backward). |
| Supports lesser number of operations in constant time | Supports additional operations like insert before, delete previous, delete current node and delete last in O(1) time. Since it supports delete last, it is used to efficiently implement Deque. |
| The SLL occupies less memory than DLL as it has only 2 fields. | The DLL occupies more memory than SLL as it has 3 fields. |
| Complexity of deletion with a given node is O(n), because the previous node needs to be known, and traversal takes O(n) | Complexity of deletion with a given node is O(1) because the previous node can be accessed easily |
| A singly linked list consumes less memory as compared to the doubly linked list. | The doubly linked list consumes more memory as compared to the singly linked list. |
| Singly linked list is relatively less used in practice due to limited number of operations | Doubly linked list is implemented more in libraries due to wider number of operations. For example Java LinkedList implements Doubly Linked List. |